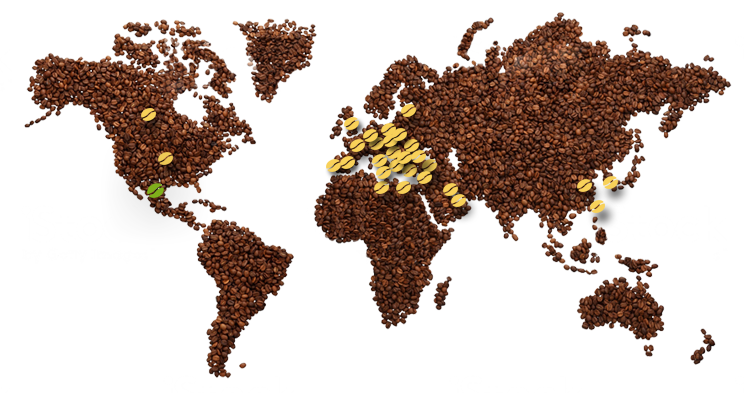
The Bean Belt, where quality coffee grows up and ripens

You may have heard the term “Bean Belt” in your favorite cafè or you may have read it on the packaging of your favorite coffee, but have you ever wondered which is the real meaning?
Well, to better explain this definition let’s undertake a journey between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. It is proper in this zone, so-called bean belt that coffee plant finds its natural habitat between 200-2000 meters of altitude, with temperatures that sways between 15 °C and 25 °C, in a warm-wet climate with lots of rains interrupted by dry seasons.
Coffee production, in the bean belt, is distributed in three big geographical area.
- Central and South America: Brazil, Colombia, Bolivia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Equador, El Salvador, Jamaica, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Dominican Republic, Venezuela, Peru, Puerto Rico.
- Africa: Ethiopia, Benin, Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Kenya, Madagascar, Central Africa Republic, Tanzania, Uganda, Sudan, Zimbabwe, South Africa.
- Asia: China, India, Indonesia, Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Vietnam, Yemen.
Only the best beans for seeding are selected and the first sprouts appear more or less after 10 weeks with part of the casing endocarp of the coffee bean.
On some plantations, once they reach a height of 5-10 centimeters, the plants are planted individually in tall vases or in plastic bags and entrusted to nurseries. In the following 4-5 months, the plants 30-40 centimeters are transplanted into the plantations.
The characteristics of coffee tree
The coffee plant is evergreen with dark-green waxy leaves and can reach 9 meters in height. However, to make easier harvesting on the plantation, the plant is pruned to reach a height of 2-3 meters.
It takes 3-4 years for a tree to become productive and the climate that characterizes tropical countries determines that coffee plants, besides to be evergreen, produce continuously. Their blossoming depends on the rains: the more they are, the more the blooms will be. As a consequence, the fruits do not ripen at the same time and it is possible to find flowers, unripe fruits and ripe fruits on the same plant.